Module 3:
HIPAA, Documentation and Safety Precautions

Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
HIPAA is a federal law that requires Protected Health Information to be kept private and secure.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) established guidelines for the use and distribution of protected health information (PHI).
Protected Health Information (PHI) includes any information about the health status, use of health care services, and payment for health services that can be linked to an individual.
This includes any patient identifiers, such as name, date of birth, medical record number, Social Security number, phone number, and address.
All treatments, assessments, test results, diagnoses, medications, and payments for services are considered confidential.
Limit discussion of confidential information among clinicians to the minimum amount of information necessary to accomplish the goal.
Furthermore, health care staff who are not directly involved in patient care are not allowed to review patient medical records unless the patient's case is being discussed during quality assurance meetings.
Patients have the right to confidentiality.
Open discussion of confidential information in public areas is prohibited.
Do not disclose confidential information to family members or friends unless authorized by the patient.
In some cases, confidential information must be reported to regulating agencies, including cases of abuse, crime, or certain infectious diseases.
Patients also have a right to accurate medical records and can ask that any errors be corrected.
Remember:
HIPAA applies to all healthcare providers
all healthcare workers must follow HIPAA regulations no matter where they are or what they are doing
penalties may be imposed for not adhering to HIPAA
A patient’s confidential information may be shared only with those staff members are working with that resident
ANSWERING THE TELEPHONE IN A LONG-TERM CARE FACILITY

Speak clearly and courteously
Identify the facility and your location per facility policy
Identify yourself by name and title
Politely ask who is calling and get contact information
Determine what is requested and transfer call to the appropriate person or take a clear message and relay it to the appropriate person as allowed under HIPAA
Thank the person for calling
Documentation:

Documentation:
One of the most critical responsibilities of all health care professionals is producing proper documentation. Documentation, is a clear and accurate method of keeping track of factual information about the resident.
This includes the needs and conditions of the resident and the care that is provided by the healthcare worker.
Why document:
Documentation allows caregivers to communicate with one another
Provides a picture of the resident’s condition
Details how the resident is responding to treatment
It is a legal record of care that can be used in a court of law
Remember:
If care is not documented, legally speaking the task was not performed
When should you document:
Documentation should occur as soon as possible after the car is provided to the resident
It is NEVER okay to document that care/services were provided prior to
being delivered to the resident
What should be documented:
You are responsible for documenting activities of daily living (ADLs) that
are outlined in each resident’s care plan.
Any other activities in which assistance is provided
Useful information that the family provides about the resident
Any refusal of assistance by the resident
Observations that are made regarding the resident
HOW TO DOCUMENT:
Accurate and complete information must be provided
Documentation must be done on time
Done in a legal manner, ensuring that all information provided is factual, without any opinions
Professional (words spelled correctly and writing is legible)
CONSEQUENCES OF INCOMPLETE/IMPROPER DOCUMENTATION:
When documentation is not completed properly, there can be serious consequences.
Legal consequences, loss of job, and loss of licensure
Changes in the resident’s condition may be overlooked
Resident’s quality of care can suffer, potentially leading to injury, hospitalization, and even death
The nursing facility may be subject to survey citations which may lead to fines or other penalties. A citation is a negative mark given when a facility fails to comply with certain requirements.
Guidelines for documentation:
Document immediately after care so you don’t forget or record inaccurate information
Think before writing your reports and document as per the patient care plan
Only write facts not opinions
If you make a mistake draw one line through mistake, mark as “error” and initial

THE OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH ADMINISTRATION (OSHA) is mandated by the government to protect all employees.
OSHA inspects LTC facilities for compliance with personal protective equipment, standard precautions, Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS), and tuberculosis testing and exposure.
OSHA also requires each facility to have an eyewash station within a reasonable distance of where hazardous chemicals are used and a total body wash station. Facility shower rooms satisfy both requirements.
PREVENTING AND MANAGING INJURIES
The safety practices taught in this class will protect both the nurse aide and the resident from injury.

The most common causes of employee injury in long-term care facilities are:
Slips and falls
Back injuries caused by improper body mechanics
Use equipment according to manufacturing guidelines and facility policy
Reporting injuries
Know and follow the facility policies for reporting injuries and emergencies of residents and staff.
All injuries should be reported and incident reports completed following facility policy.

SAFETY IS EVERYONE’S CONCERN
Some older individuals may not realize that some activities may be harmful to them. Communicate with residents about safety while maintaining his/her right to choices about care and activities.
The resident has the right to a safe environment. A safe environment is a place where a resident can ambulate and carry on his daily activities without obstacles or hazards that may result in injury or death. Think about safety first when you enter an area and last when you leave the area.
POTENTIAL PHYSICAL CHANGES IN THE ELDERLY THAT INCREASE THE RISK OF ACCIDENTS ARE:
Decreased vision
Impaired hearing
Slower reflexes
Mental changes such as forgetfulness or confusion
Weakness due to illness, injury, or shrinking of unused muscles
The most common cause of accidents for LTC residents is falls
GUIDELINES FOR PROVIDING A SAFE ENVIRONMENT
Recognize and report unsafe conditions that nurse aides are unable to correct.
Keep hallways and resident rooms clean, dry, and free of obstacles.
Keep equipment and supplies on one side of the hallway so that residents have an unobstructed path
Pick up any objects on the floor
Wipe spills immediately and place a wet floor sign
Keep beds in prescribed position and wheels locked
Maintain adequate lighting
Provide call signals to all residents and remind residents to call for help
Report all equipment not in proper working order and use it according to facility policy and manufacturer’s directions.
Unsafe or broken equipment should be identified and removed from service according to facility policy.
ACCIDENT AND INCIDENTS
Incident
an accident or an unexpected event during the course of care that is not part of the normal routine in a healthcare facility i.e. falls, lacerations, burns
Accident
An unexpected situation which cause injury, damage of property or any other undesirable event.
The following events are considered incidents:
Falls
equipment broken or damaged
injuries
accusations against staff
blood or body fluids exposure
Your role as a healthcare worker is recognizing and reporting incidents and accidents, UNSAFE OR BROKEN EQUIPMENT should be “locked out” so that it cannot be used.
The person who discovers broken equipment should “tag” and remove the equipment as per facility policy.
Remember these guidelines for incident reporting:
explain what happened
State only facts
describe what you did in the situation
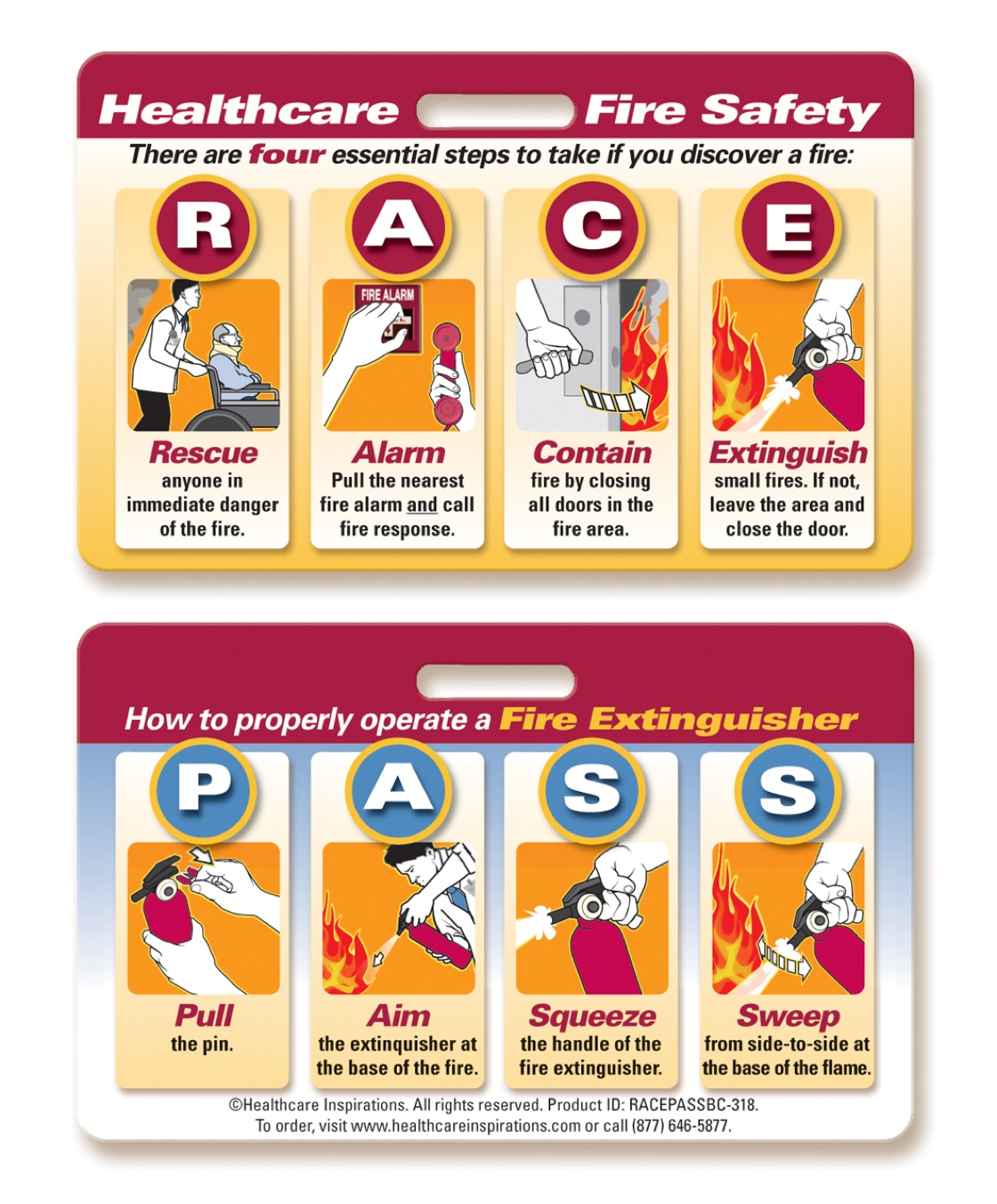
Fire Safety

This is how NA’s play a role in fire safety:
Never leave smokers unattended
Report any potentially dangerous situation
Report if fire alarm or exit doors are blocked
In case of fire, use the acronyms RACE and PASS